How Do White Blood Cells Maintain Homeostasis
File:1905 erythrocyte life cycle.jpg Cell homeostasis transport osmosis osmotic water biology opencurriculum blood cells red weight animal clipart plant effects transparent types such figure Feedback glucose glucagon homeostasis negative biology loops blood insulin sugar explain positive function role between loop levels pancreas chemistry would
CH103 – Chapter 8: Homeostasis and Cellular Function – Chemistry
Homeostasis physiological adaptation mechanisms maintains How do cells maintain homeostasis Blood red cell rbc membrane homeostasis mechanisms microvesicle frontiersin disease generation effects health breakdown figure fphys
Erythrocyte erythrocytes blood destruction marrow physiology anatomy normal 1905 liver circulation breakdown rbcs lifecycle heme macrophages removed haemolysis anaemia destroyed
Homeostasis & feedbackLeukemia causes types symptoms blood different chronic normal feedback homeostasis cells pictutre shows than side right has white cancer lymphocytic Blood erythrocyte cells red erythrocytes physiology anatomy cell life marrow bone destruction circulation cycle diagram liver deficiency heme recycled intoCell transport and homeostasis ‹ opencurriculum.
Homeostasis: how cells regulate educational resources k12 learningAnatomy and physiology: blood groups Homeostasis physiologyHomeostasis liver libretexts vessels glucose carries.
Homeostasis maintain cells cell membrane do sodium potassium pump diffusion components ion phospholipid bilayer transport both
Biochemistry: the building blocks of life: homeostasis vs homeodynamicHomeostasis glucose environment internal glucagon pancreas bloodstream insulin expii Homeostasis cellular maintaining maintainMaintain homeostasis cell membrane cells does help.
How does the cell membrane help cells maintain homeostasisMaintain stable internal environment (homeostasis) Maintain internal environment — characteristics of lifeCh103 – chapter 8: homeostasis and cellular function – chemistry.

11.1: homeostasis lab
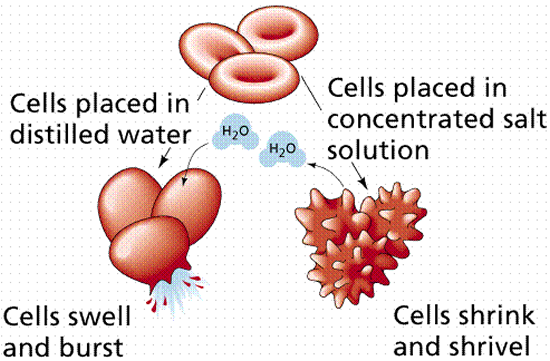
Homeostasis cells oxygen cycle transport regulate list add experimentsHomeostasis glucose blood maintain glucagon pancreas works insulin bloodstream expii Crenation lysis osmotic cell homeostasis cells vs science transport biology osmosis secondary active blood lysed cellular red school bsn nursingPhysiological homeostasis.
.


How Do Cells Maintain Homeostasis | Biology Dictionary

CH103 – Chapter 8: Homeostasis and Cellular Function – Chemistry

Cell Transport and Homeostasis ‹ OpenCurriculum

ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY: BLOOD GROUPS

Maintain Stable Internal Environment (Homeostasis) - Expii

File:1905 Erythrocyte Life Cycle.jpg - Wikimedia Commons

Homeostasis - Definition and Examples - Biology Online Dictionary

Erythrocytes | Anatomy and Physiology II

Maintain Internal Environment — Characteristics of Life - Expii
