How Does Blood Maintain Homeostasis Examples
What is homeostasis |the garden of eaden Main mechanisms of homeostasis What is homeostasis
5. Homeostasis and response - THOMAS TALLIS SCIENCE
Homeostasis glucose internal stable food glucagon pancreas insulin bloodstream expii Homeostasis mechanisms body main homeostatic blood mechanism pressure temperature Ch103 – chapter 8: homeostasis and cellular function – chemistry
Homeostasis water body human illustration temperature system within maintains mechanism essential types role narrow limits amount its graphic model changes
Maintain stable internal environment (homeostasis)What is homeostasis? » scienceabc Maintain stable internal environment (homeostasis)5. homeostasis and response.
Homeostasis body blood mechanisms response feedback maintain regulation science internal regulate sugar explain conditions external changes cell h2o organismHomeostasis glucose environment internal glucagon pancreas bloodstream insulin expii Homeostasis cellular function feedback temperature chemistry regulation homeostatic positive fever humans ch103 coreHomeostasis feedback control effector receptor human environment things simple sensor homeostatic components negative system body mechanisms anatomy maintain cells centre.


Maintain Stable Internal Environment (Homeostasis) - Expii
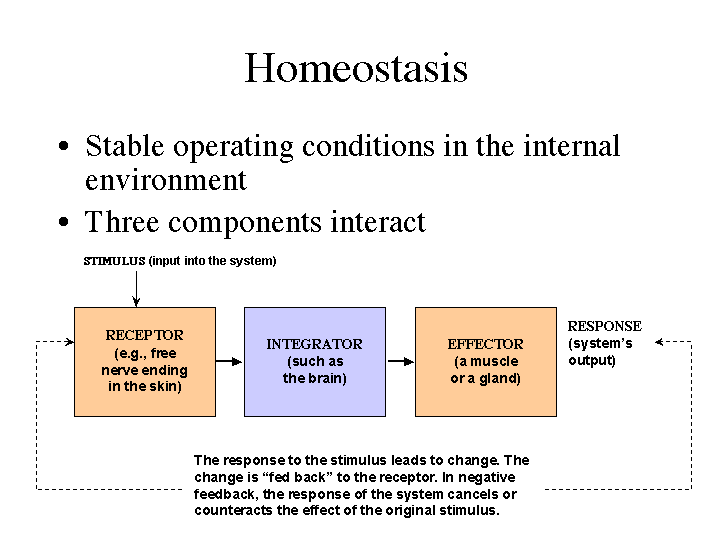
WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS |The Garden of Eaden

Homeostasis - Definition and Examples - Biology Online Dictionary

Maintain Stable Internal Environment (Homeostasis) - Expii

What Is Homeostasis? » ScienceABC

What Is Homeostasis | Its Essential Role & Types in Human Body

CH103 – Chapter 8: Homeostasis and Cellular Function – Chemistry

Main mechanisms of Homeostasis - Homeostasis

Homeostasis - Definition and Examples - Biology Online Dictionary
